As Australia hurtles towards COVID-19 vaccination levels that would put it among the highest in the world, the question now for the immunisation program is – what’s next?
As a result, media attention has been pulled towards debates on long-term efficacy and booster shots.
Those nations at a more advanced stage are beginning to offer real-world evidence on this topic, and it looks like the media are about to become interested in antibody testing.
A number of studies emerging around the world suggest protection against infection wanes within just a couple of months after full vaccination, while protection against hospitalisation and death holds steady.
Data from our monitoring software, Meltwater, shows media mentions of terms referencing “waning protection” and “breakthrough infection”, have risen 169% in the last 90 days in comparison to the previous quarter.
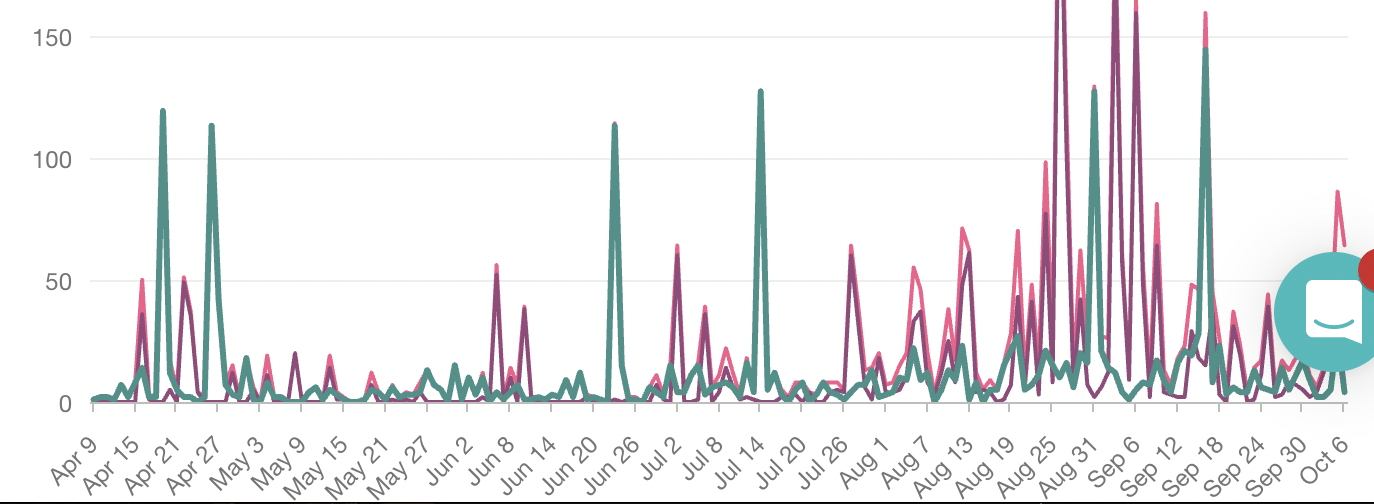
Unsurprisingly, the word “Delta”, referencing the more infectious strain, has appeared more than any other term. This is because scientists suspect the Delta strain is more effective at evading vaccines than previous strains, although evidence for this remains inconclusive.

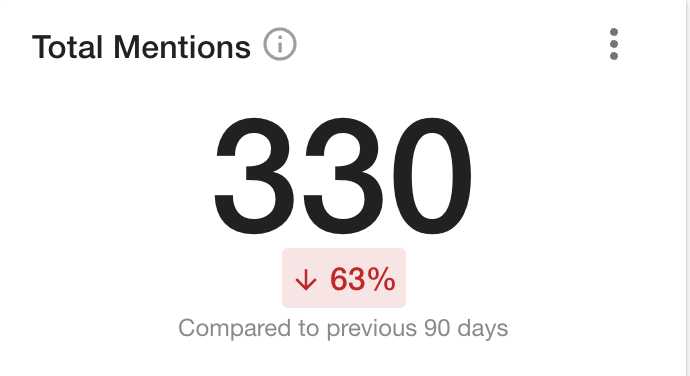
Mentions of antibody testing in the media are down over the last 90 days. And while that might come as a surprise, it means it could emerge as an attractive, new angle for journalists.
Antibody test manufacturers, laboratories and clinicians, could expect more inquiries in the coming months.
Dean Whiting, CEO Pathology Technology Australia said: “Currently there are COVID-19 antibody tests approved and available in Australia from a number of the world’s major manufacturers. These tests are performed on automated test platforms in Australia’s registered pathology laboratories.”
“Many of these tests have been evaluated against the recently published International Guidelines for testing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and found to perform extremely well. Most showing close to or on 100 per cent accuracy and displaying excellent reproducibility.”
“The measurement of anti-COVID-19 antibodies can be used to assess if an individual has developed immunity to the SARS-CoV-2 virus – so called seroconversion. Measurement of antibodies can also tell us if immunity has waned over time. Antibodies to the viral spike and nucleocapsid proteins are available and manufacturers offer various combinations of IgM, IgG and Total Ig antibody detection.
“This means that we can detect the immune system’s early response (within 7 to 12 days of exposure) to the virus or vaccination, as well as detecting the longer term immunity (14 days or more after infection or vaccination).”